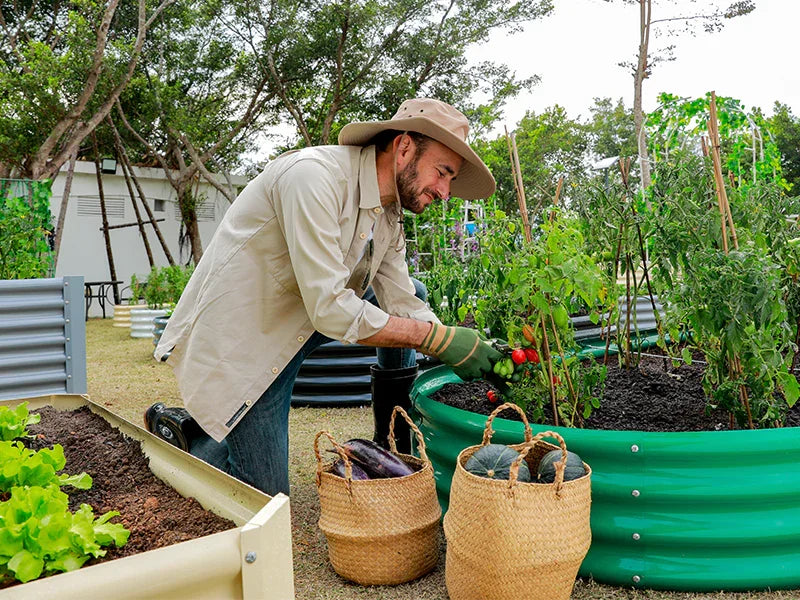
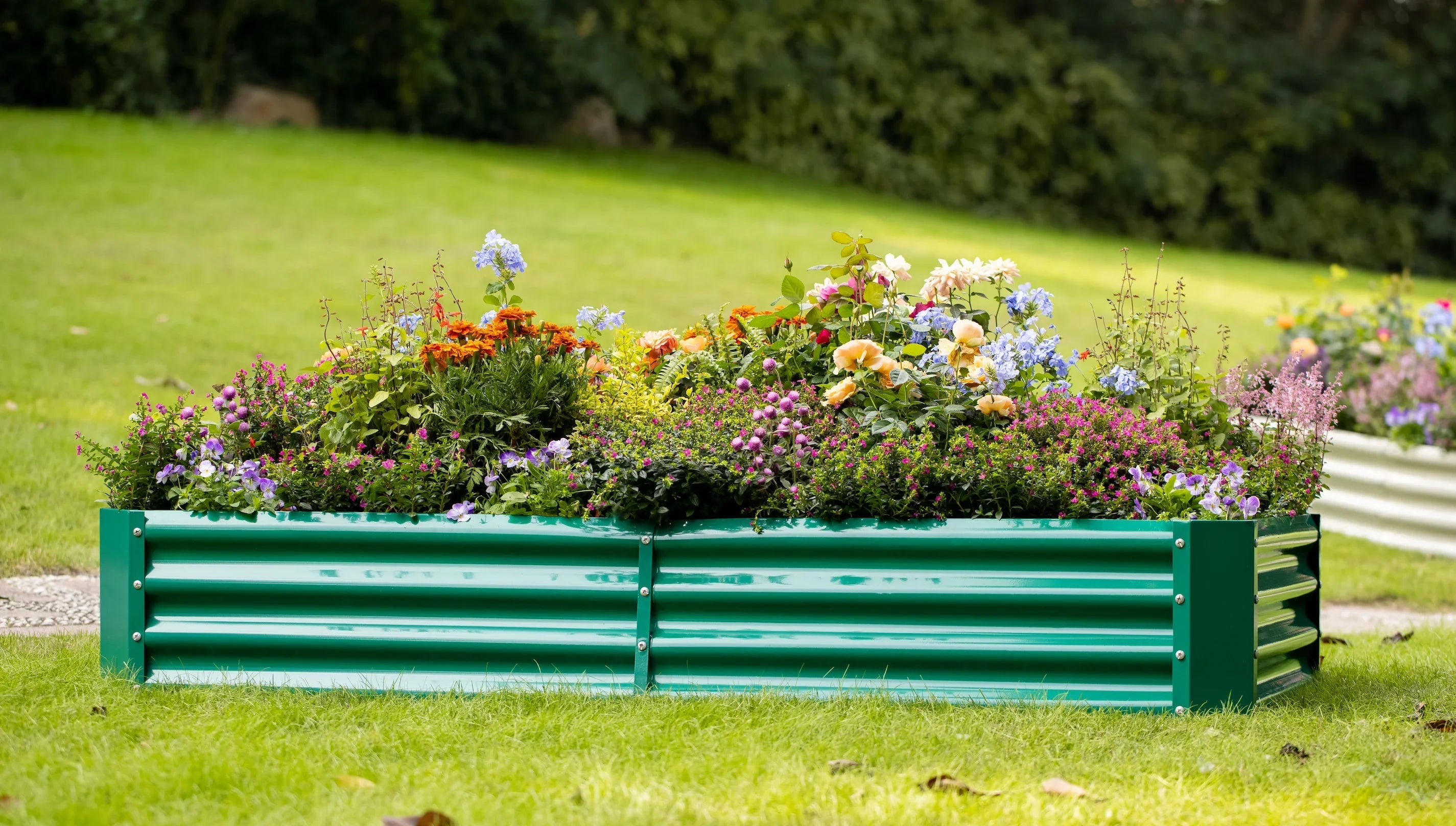
Gardening is one of the most rewarding hobbies, and using garden beds effectively can dramatically improve the health and yield of your plants. Whether you’re a gardening newbie or someone looking to refine your skills, understanding how to make the most of your garden bed is crucial. In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about garden beds, from selecting the right type to planting tips for maximizing growth and yield.
1. Choosing the Right Garden Bed
Types of Garden Beds
Garden beds come in various forms, each with its unique advantages. For example, raised garden beds provide better drainage, reducing the risk of overwatering, and are perfect for growing vegetables and herbs. Raised beds also offer more precise soil control, which is ideal for areas with poor soil quality.
For smaller spaces, modular garden beds are a great choice. These can be stacked or arranged in various shapes, offering flexibility and adapting to different layouts. Traditional in-ground garden beds, on the other hand, provide more room for roots to spread but require more maintenance to improve soil fertility.
Material Choices
When choosing a garden bed, material matters. Common materials include wood, stone, metal, and plastic, each varying in durability, aesthetics, and cost. For instance, cedar wood is naturally resistant to decay and pests, making it a top choice for raised beds. If you prefer a more modern look, galvanized steel or weathered steel garden beds can add an industrial flair to your garden while being long-lasting.
2. Garden Bed Tips: Maximizing Plant Health and Yield
Planting Layout: Companion Planting
One of the best ways to ensure your plants thrive in garden beds is through companion planting. Some plants grow better together, enhancing each other’s growth, repelling pests, or even improving flavor. For example, basil and tomatoes are often planted together to boost the flavor of tomatoes and deter pests like aphids. Similarly, marigolds planted with vegetables can repel harmful insects with their strong scent.
Additionally, consider the growth habits of plants when designing your garden bed layout. Tall plants like sunflowers should be placed on the north side of your garden bed to avoid shading shorter plants. Low-growing plants, such as herbs and leafy greens, should be placed on the southern side to maximize sun exposure.
Soil Health: The Importance of Soil Preparation
The health of your soil directly impacts plant health. Before planting, enrich the soil by adding organic matter such as compost, manure, or leaf mold. Organic materials improve soil structure, enhance drainage, and help retain moisture, providing the nutrients plants need to thrive.
If you’re using raised garden beds, make sure the soil is deep enough for root expansion. Most vegetables need at least 12 inches of soil depth, while deep-root crops like carrots and potatoes may require more.
Fertilizing: Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Your Plants
Different plants have varying nutrient needs. For instance, leafy greens like spinach or lettuce require nitrogen-rich fertilizers to promote leaf growth. On the other hand, fruiting plants like tomatoes and peppers need more phosphorus to support flowering and fruiting.
For organic gardening, consider using slow-release organic fertilizers like bone meal, blood meal, or composted chicken manure. These fertilizers break down gradually, providing plants with a steady supply of nutrients without overwhelming them.
3. Maintaining Your Garden Bed: Regular Care and Upkeep
Watering: Maintaining Consistent Moisture
Proper watering is one of the most critical aspects of garden bed maintenance. Too much water can cause root rot, while too little can stress plants and stunt their growth. A good rule of thumb is to water deeply but infrequently, ensuring moisture reaches the root zone. Raised garden beds tend to dry out faster, so they may require more frequent watering.
If you live in a hot climate, consider installing a drip irrigation system to deliver water directly to the roots, reducing water waste.
Weeding and Mulching: Preventing Weed Growth
Weeding is an ongoing task in any garden, and garden beds are no exception. Weeds compete with plants for nutrients, water, and sunlight. Mulching is an effective method for suppressing weed growth. Organic mulches, such as straw, wood chips, or shredded leaves, not only block weeds but also help retain soil moisture and regulate soil temperature.
Be sure to replenish the mulch layer regularly. A 2-3 inch layer of mulch is typically enough to keep weeds at bay.
Pest Control: Protecting Your Garden from Pests
Even the healthiest garden beds can fall victim to pests. To control pests organically, plant garlic or onions—both of which have natural pest-repellent properties. You can also use row covers to create a physical barrier against flying insects.
For more severe pest issues, consider using insecticidal soap or neem oil, both of which are safe for plants and the environment.
4. Boosting Garden Bed Efficiency: Using Garden Accessories
Garden Trellises and Supports
Using garden accessories, like garden trellises or plant supports, can significantly enhance the productivity of your garden bed. These accessories allow climbing plants like cucumbers, peas, and tomatoes to grow upward, saving space and making harvesting easier. Trellises also keep fruits off the ground, reducing the risk of rot and pest damage.
Plant Supports and Row Covers
For tall or heavy plants, use plant supports to prevent them from falling over. Row covers can also protect your plants from pests and harsh weather conditions, ensuring they grow strong and healthy throughout the season.